
II. Soft Robots (SMA based) | |||
| Soft robots may potentially be used for human services and complex environmental locomotion. The bodies of the soft robots are made from soft materials to make them safe for human interactions and to enable them to deform enough to adapt to soft or rough terrains. | |||
II.1 SMA Pectoral Fin | |||
 | Pectoral fins play an important role in the fish swimming performance,especially in maneuverability underwater This work presents the swimming propulsion by means of a flexible and lightweight pectoral fin inspired by a Koi Carp. The fin is driven by embedded shape memory alloy (SMA) wires. | ||
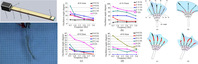 | |||
| SMA fin ray / The bending angle of SMA fin ray under different conditions / SMA fin with variable shapes | |||
Design and Implementation of a Lightweight Bio-Inspired Pectoral Fin with Complex Motions. Shiwu Zhang*, Bo Liu, Qin Yan, Lei Wang, K.H. Low, and Jie Yang. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics. Vol. 19(6), 1773-1785, 2014 | |||
Dynamic Characteristics of Planar Bending Actuator Embedded with Shape Memory Alloy. Yong Du, Bo Liu, Min Xu, Erbao Dong, Shiwu Zhang*, Jie Yang. Mechatronics. Vol.25 pp.18-26, 2015 | |||
| A Novel Implementation of a Flexible Robotic Fin Actuated by Shape Memory Alloy. Qin Yan, Lei Wang, Shiwu Zhang* and Jie Yang. Journal of Bionic Engineering. vol 9, no. 2. pp. 156-165, 2012 | |||
II.2 Soft SMA Arm | |||
 | The practical applications of SMA soft robots are limited because their body stiffness is too low and the deformation is continuous, which make it diffcult to control their movements. In this work, the design and implementation of a soft robotic arm driven by shape memory alloy (SMA) coils are reported. The precision control of the SMA arm was realized based on feedback signals from the embedded Hall sensors. This soft robotic arm can follow a two-dimensional motion with a relatively high accuracy; indeed, it displays quite a remarkable performance considering its low cost, simple structure, easy control, and small bending error. Since this soft arm can be used as the basic driving unit of a soft robot capable of manipulating and locomoting, it has shed light on the applications of SMA soft robots. | ||
 | |||
| SMA soft arm performs a step bending motion and a two dimensional circular motion | |||
| Design and Implementation of a Soft Robotic Arm Driven by SMA Coils, Hao Yang, Min Xu*, Weihua Li and Shiwu Zhang*. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics 66(8): 6108-6116, 2019; Video can be download from IEEE Xplore Digital Library | |||
II.3 SMA Planar actuator | |||
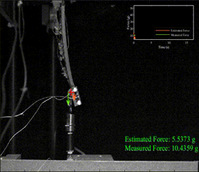 | Shape memory alloys (SMAs) have advantages of high power-to-weight ratio, silent operation, and high response speed, which make them suitable for fabricating soft, compact, and muscle-like soft actuators with various transformation capabilities. However, it is challenging to precisely control SMA-based soft actuators and robots because of the lack of explicit dynamics-based control method. In this article, a linear phase transition model of SMA is derived to express the dynamic model of an SMA planar actuator (SPA) in an explicit form. Then, a model-based feedback controller considering constraints of strain of the SMA, temperature increment of the SPA, and load increment was built. Strain gauges are used to obtain the bending angle of the SPA as the feedback signal for the controller. Various capabilities of the SPA, such as step response, position tracking with constant angular speed, and motion control with load, were experimentally evaluated. The developed method is meaningful for modeling and control of various SMA-based actuators and robots. | ||
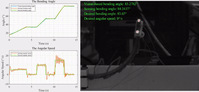  | |||
| Speed Control of an SMA planar actuator/ SMA planar manipulator grasps various objects and measures their weight | |||
| Modeling and Motion Control of a Soft SMA Planar Actuator, Hu Jin; Yiming Ouyang; Haoyao Chen; Jingwen Kong; Weihua Li*; Shiwu Zhang*, IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics 27(2):916-927,2021.Video can be download from IEEE Xplore Digital Library | |||
| Shape and Force Sensing of a Soft SMA Planar Actuator for Soft Robots, Yiming Ouyang, Hu Jin*, Haoyao Chen, Jingwen Kong, Weihua Li, Shiwu Zhang*, IEEE Robio, 2021. (Best student paper final list) | |||
II.4 Dexterous Hand | |||
 | |||
| Coming soon | |||